Managing LLM Conversations Using a Graph Structure

Introduction
Ever felt frustrated when a chatbot loses context after you explore a side topic? Current LLM (Large Language Model) conversation models are limited by their linear structure, which hinders context preservation and flexibility in branching and merging conversations. To overcome this, I propose a graph-managed LLM conversation approach, allowing for broader discussions with specific side topics while maintaining the full context.
Setting the Glossary
The Conversation Node
In human-LLM conversations, the basic building block is a question-answer (or input-output) pair. We’ll refer to this as a conversation node.
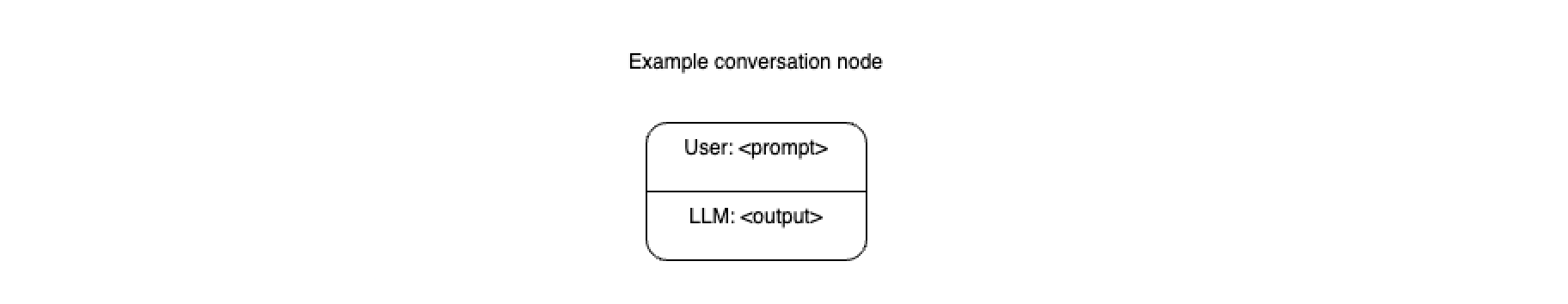
Conversation History
A sequence of conversation nodes forms a conversation history. This history can be authentic (real input-output pairs) or fabricated (synthetic data).
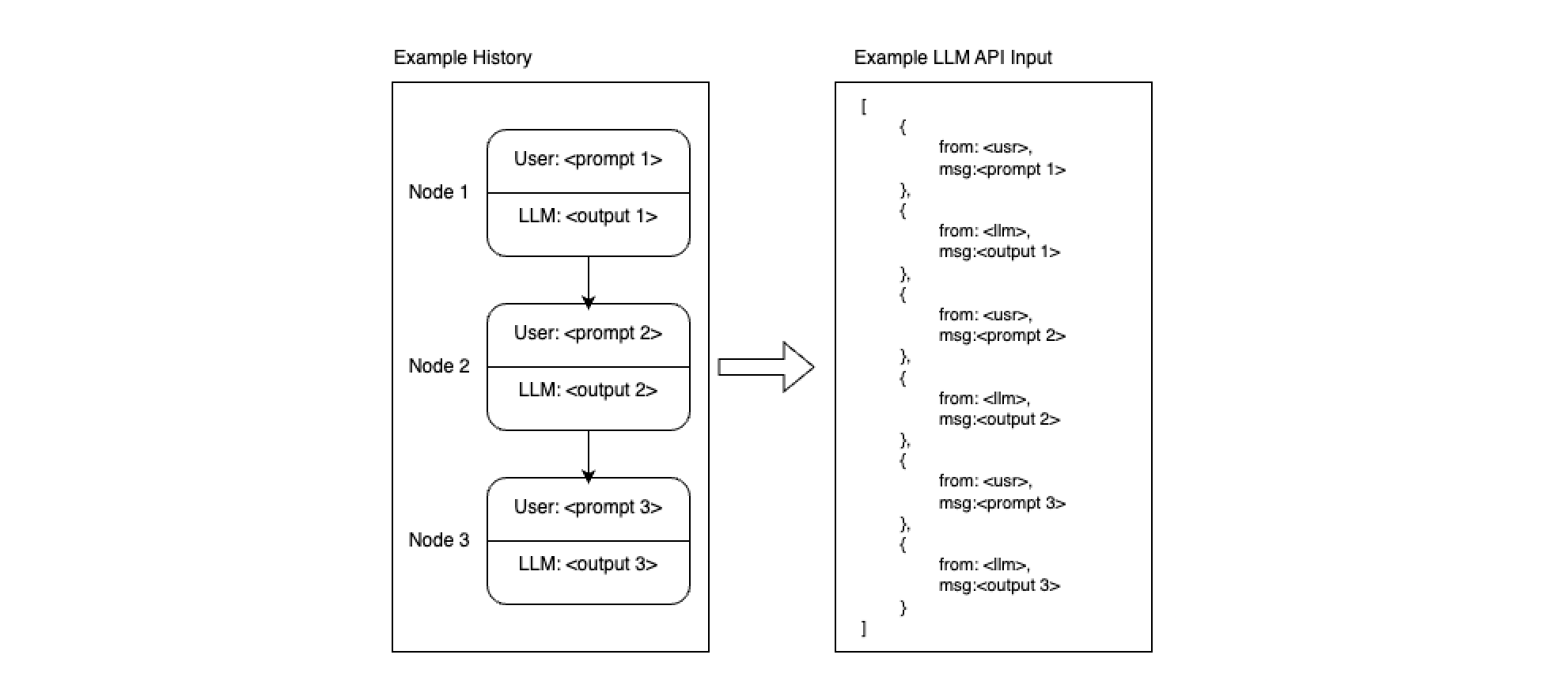
Transforming Conversation History into API Input
The sequence of conversation nodes is typically converted into a JSON format to be used as input for an LLM API. This process is open to manipulation.
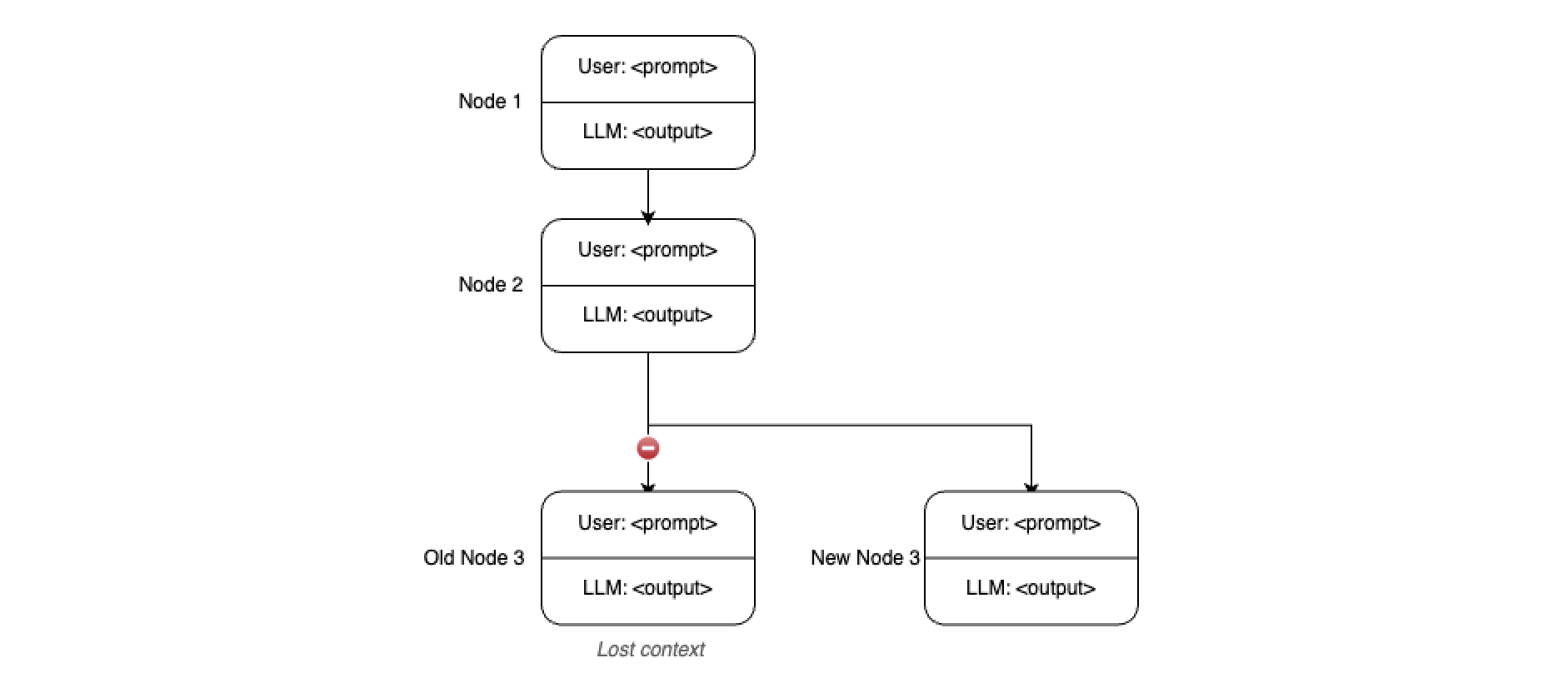
Branching Conversations
When branching off from an earlier node, the context from the existing branch is often lost, which is expected. However, exploring new concepts in a new branch can be useful. Eventually, you might want to return to the main conversation, but its context remains isolated from the current branch.
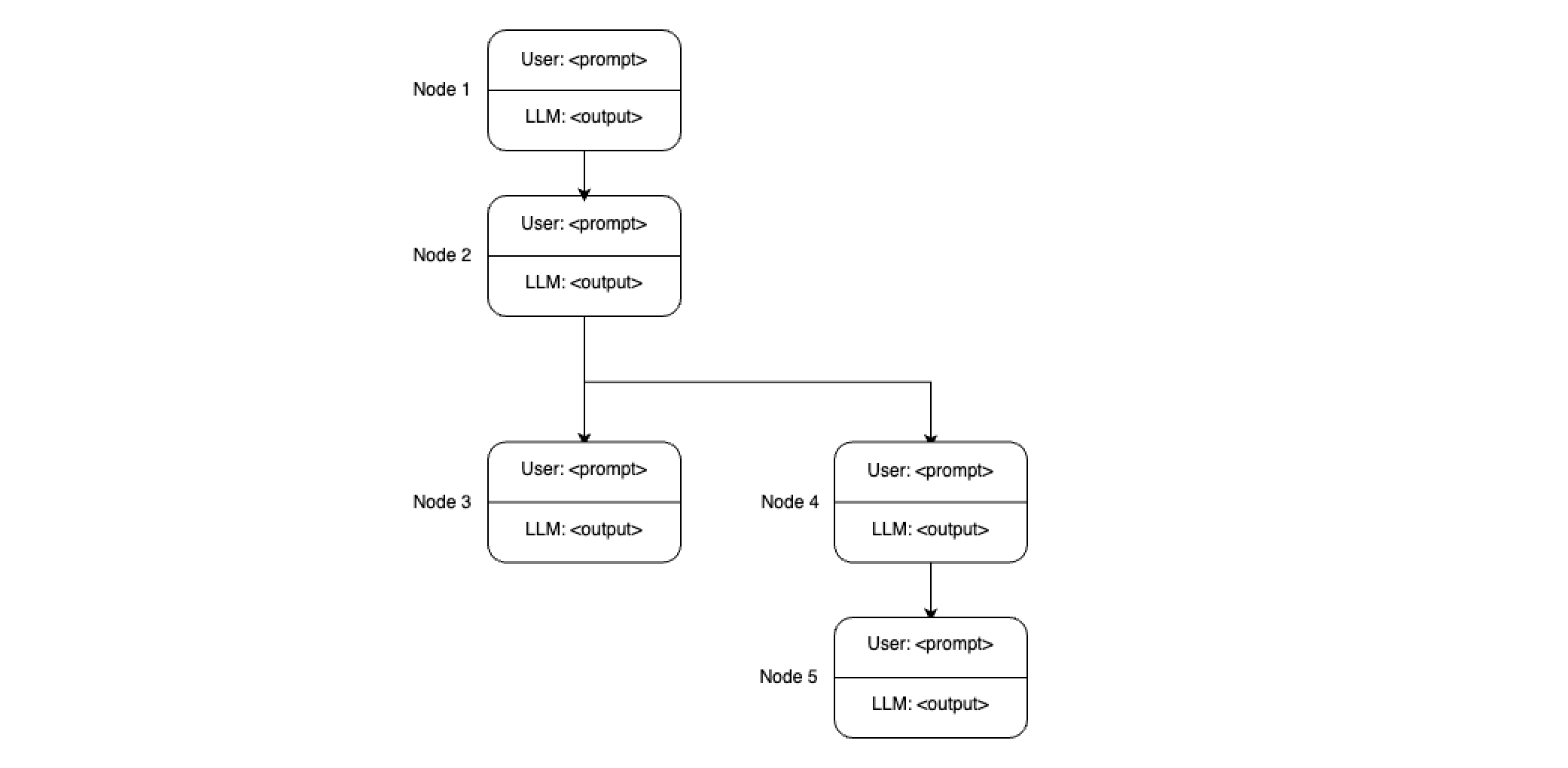
Proposal
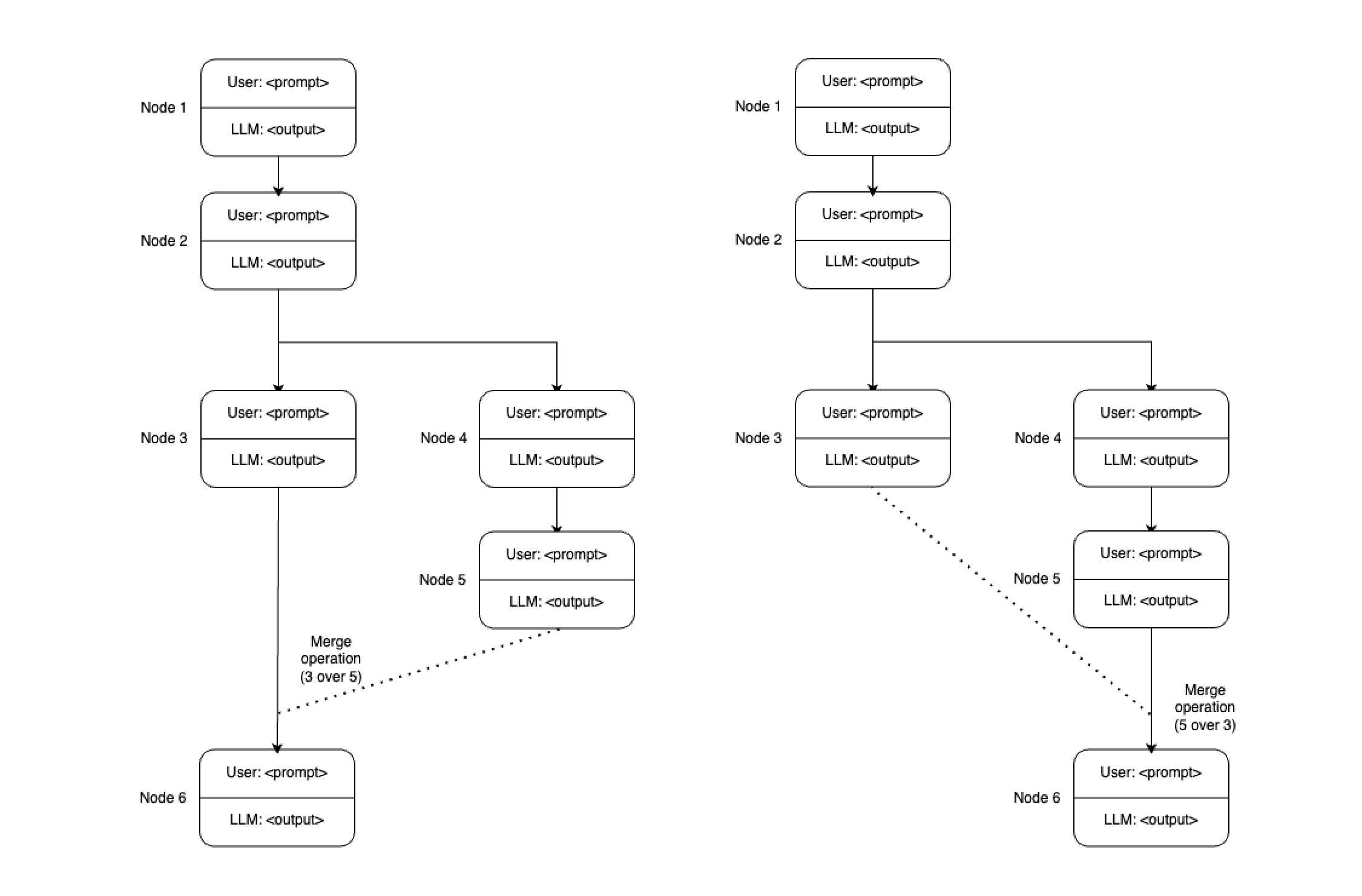
Merging Priorities
To merge two or more branches back into a single conversation, the order of merging is crucial as it affects the LLM’s context. Users should have the ability to specify the order of merging, effectively setting the priority of each branch.
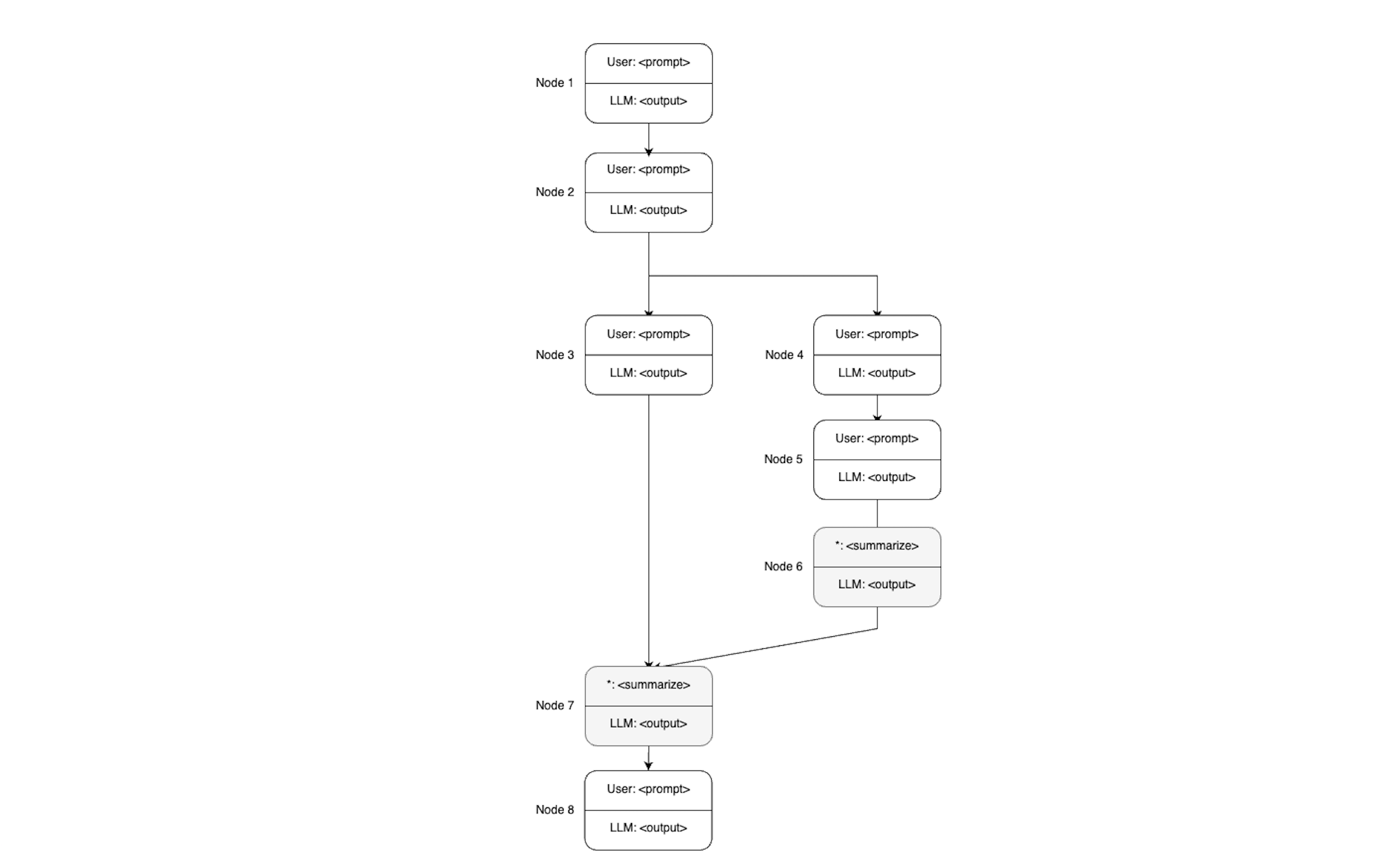
Background Summarization and Prompt Compression
During the merging of branches, the LLM may have too much context to consider. To manage this, techniques such as background summarization can rebase the deprioritized branch closer to the prioritized one. Prompt compression, like the LLMLingua method, can also help manage the context effectively.
Conclusion
Graph-managed LLM conversations enable broader discussions with specific side topics while maintaining full context, much like human-to-human conversations. This approach improves the context-awareness of LLM agents, allowing for more precise and in-depth discussions.
By adopting graph-managed conversations, you can explore various topics in depth without losing context, ultimately enhancing your interaction with LLMs. I am yet implement this as an MVP but feel free to experiment with this approach and share your experiences!
